
AWS SaaS
SaaS
SaaS, or Software as a Service, is a cloud computing model where software applications are provided over the internet on a subscription basis. Instead of installing and maintaining software locally, users can access the applications through a web browser. SaaS eliminates the need for users to handle tasks like software updates, maintenance, and support, as these responsibilities are managed by the SaaS provider. It offers a convenient and scalable solution for businesses to access and use software without the complexities of traditional software deployment.
FUNDAMENTALS OF SaaS
Cloud Delivery: Software accessed over the internet.
Subscription Model: Pay-as-you-go instead of ownership.
Managed Maintenance: Provider handles updates and support.
Scalability: Easily adjust usage based on needs.
Anywhere Access: Web browser accessibility.
Cost Efficiency: Reduced infrastructure costs.
Automatic Updates: Seamless integration of new features.
Collaboration: Promotes teamwork and sharing.
Shared Resources: Optimizes cloud infrastructure.
User-Focused: Emphasizes a hassle-free user experience.
TYPES OF SaaS:
Based on industry: Horizontal and Vertical SaaS Architecture
Horizontal SaaS Architecture:
Horizontal SaaS architecture is intended to serve users from many industries. They offer a spectrum of innovative and integrated features, as well as guaranteed security and performance requirements, attracting worldwide organizations from various industries. Software behemoths such as Salesforce, Microsoft, and AWS provide users with a horizontal SaaS architecture via which they may access numerous capabilities based on their needs.
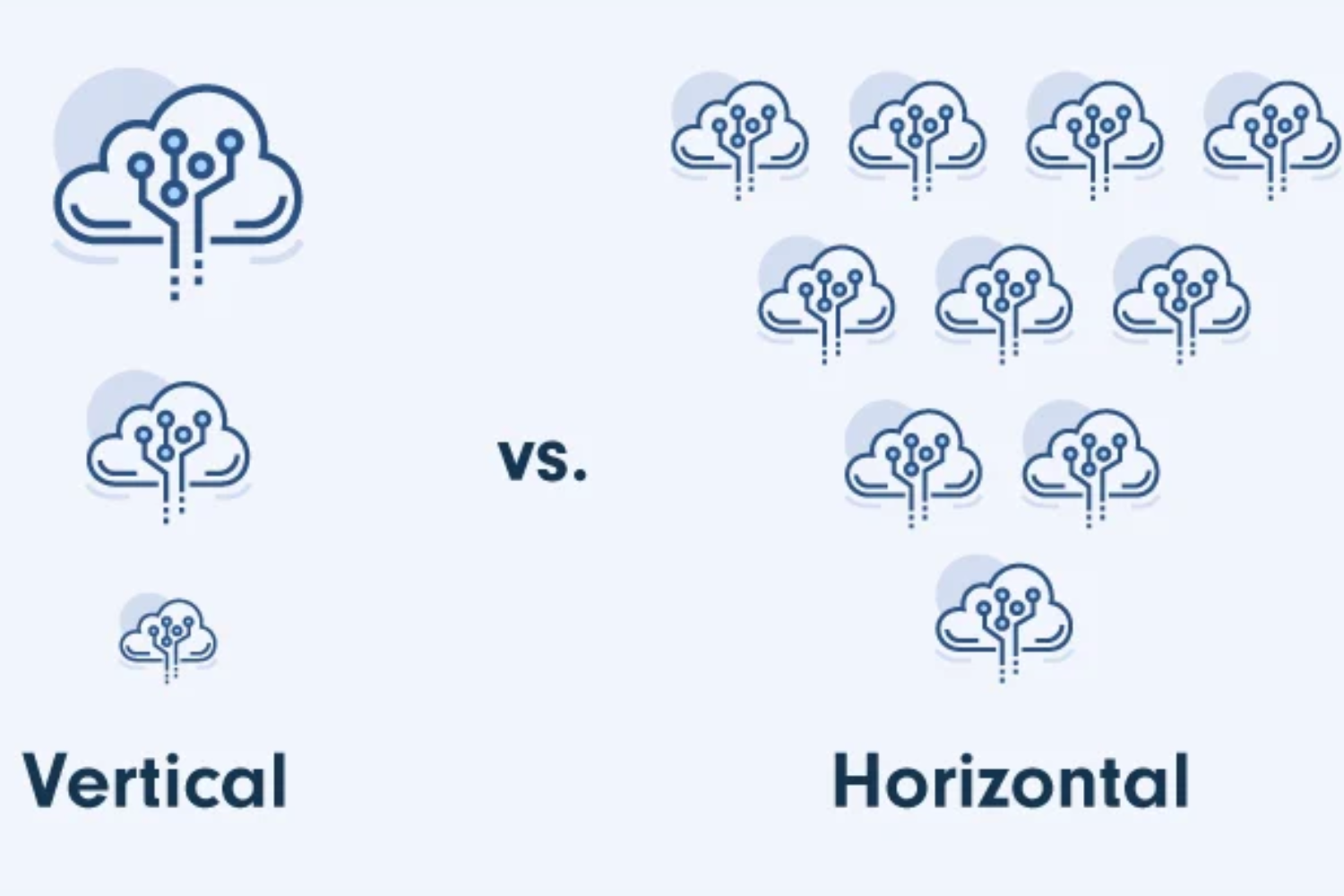
Vertical Software as a Service Architecture:
Vertical SaaS architecture, in contrast to the horizontal approach, is planned and created for a single industrial vertical or function. It entails directing an ecosystem with deep expertise to meet the needs of a specific niche. This architecture may not have a large feature set, but it is designed to answer a specific industry need. SaaS providers such as Guidewire and IBM provide solutions tailored to a specific industry challenge.
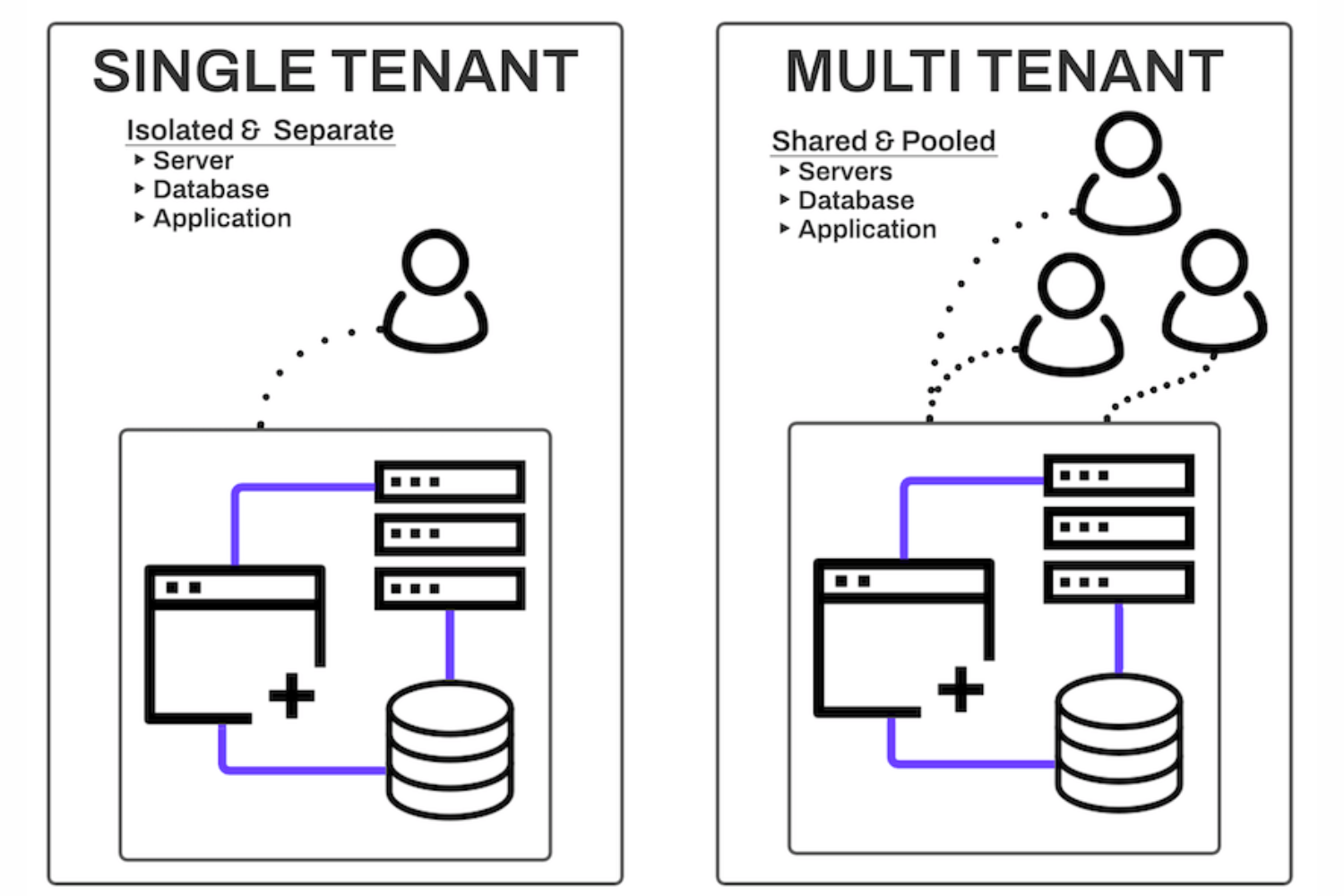
Based As Per Tenancy: Single-Tenant and Multi-Tenant SaaS Architecture
Single-Tenant SaaS Architecture :
Everything in a single-tenant SaaS architecture is customized to meet the needs of a single buyer, and resources cannot be shared with other customers. Each user has their own server, infrastructure, and database. Each tenant’s data is thus segregated from one another.
Multi-Tenant SaaS Architecture:
This architecture is the most popular among multinational corporations since it is cost-effective and supports a wide range of use cases. Multiple instances of a program run in a shared environment in this design. Tenants share a database, infrastructure, and other assets. The display, data setting, and rules are the same for all buyers.
BENEFITS OF SaaS
Cost Efficiency: Eliminates upfront investment in software and hardware.
Scalability: Easily adjusts to changing user and business needs.
Automatic Updates: Ensures access to the latest features and security patches.
Accessibility: Enables users to access applications from any location with internet access.
Managed Maintenance: Providers handle software updates, maintenance, and support.
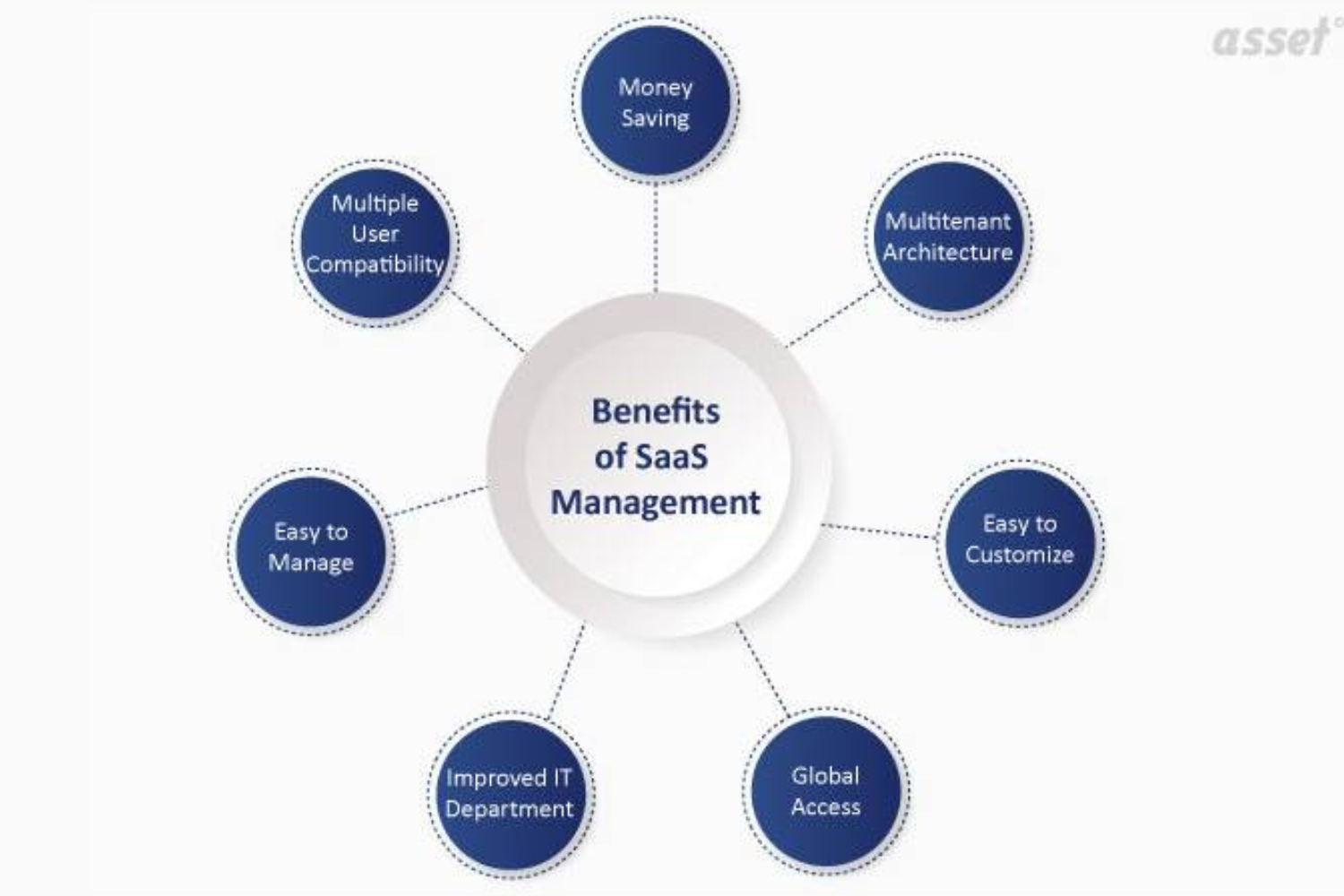
Flexibility: Allows for seamless integration with other cloud services.
Collaboration: Promotes teamwork with shared, accessible applications.
Focus on Core Business: Frees up resources for core business functions.
Global Access: Supports remote work and global teams.
Reduced IT Burden: Shifts infrastructure management to the SaaS provider, reducing IT workload.
JOB ROLES OF SaaS
1. SaaS Developer
2. SaaS Administrator
3. SaaS Sales Specialist
4. Customer Support Analyst
5. Data Security Specialist
6. Integration Engineer
7. SaaS Consultant
8. Product Manager
9. User Experience (UX) Designer
10. SaaS Analyst
SALARY: The salary is between 13LPA TO 35LPA
TECHNOLOGIES OF SaaS
Cloud Computing: SaaS relies on cloud infrastructure for remote access to applications.
Web Development Technologies: HTML, CSS, and JavaScript create user interfaces for SaaS applications.
Virtualization: Optimizes server resources for efficient sharing among multiple users.
Multitenancy Architecture: Enables a single instance to serve multiple users securely.
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces): Facilitate integration and data exchange between SaaS applications.
Security Technologies: Encryption, SSL, and secure protocols protect data during storage and transmission.
Database Management Systems (DBMS): Store and manage user data efficiently.
Identity and Access Management (IAM): Controls user access through SSO and multifactor authentication.
Monitoring and Analytics: Track performance, identify issues, and gather insights for optimization.
Containerization and Orchestration: Docker and Kubernetes enhance deployment flexibility and scalability in SaaS environments.
COURSE HIGHLIGHTS
1. Suited for students, fresher’s, professionals, and corporate employees
2. Live online classes
3. 4-Month program.
4. certificate of completion
5. Decision Oriented Program of Analysis
6. Live Classes by highly experienced faculties
7. Hands-on experience with real-life case studies

CONCLUSION
In conclusion, Software as a Service (SaaS) represents a transformative model in the software industry, offering users access to applications and services on a subscription basis rather than traditional ownership. This cloud-based approach provides numerous advantages, including cost-effectiveness, scalability, and seamless updates, while reducing the burden of maintenance and infrastructure management on users. SaaS has become a cornerstone in the digital landscape, enabling organizations to streamline operations, enhance collaboration, and adapt to rapidly evolving technological landscapes. As businesses increasingly embrace the benefits of SaaS, the model is poised to continue shaping the future of software delivery and consumption.

